Capstone Cozamin Mine to Average Over 51 MIbs Cu for 10 Years; Initiates “Impact23” Project for Further Growth

(All amounts in US$ unless otherwise specified)
VANCOUVER, British Columbia–(BUSINESS WIRE)–#LOMP–Capstone Mining Corp. (“Capstone” or the “Company”) (TSX:CS) announces an updated Technical Report for its Cozamin Mine in Zacatecas, Mexico and extends mine life to 2031. Mineral Reserves increased by 39% to 14.1 million tonnes grading 1.77% copper and 44.4 grams per tonne (g/t) silver and Indicated and Inferred Mineral Resources increased by 10% to 29.7 million tonnes grading 1.52% copper and 44 g/t silver. The new reserve mine plan is projected to produce 512 million pounds of copper and 16.0 million ounces of silver over the next 10 years.
HIGHLIGHTS
- Updated life of mine plan (“LOMP”) released. Average annual copper production of 51.2 million pounds of copper and 1.6 million ounces of silver production over 10 years at average C1 costs, including the 50% silver stream, of $1.02 per payable pound of copper. From 2021 to 2027, average annual production is 58.8 million pounds of copper and 1.7 million ounces of silver. Average projected C1 costs over this period are $0.96 per payable pound of copper.
- Ramp-up to 3,780 tonnes per day (“tpd”), or 1.38 million tonnes per annum (“tpa”), by the end of Q1 2021 is on track. A new section of ramp to open the one-way traffic circuit to debottleneck the mine was completed in early December 2020, ahead of schedule.
- Estimated Reserves increased by 39% to 14.1 million tonnes, relative to April 30, 2020; contained copper and silver increased by 37% and 49%, respectively. Approximately half of this increase is due to recovery of high-grade pillars using paste backfill.
- Tailings management transformation activities are progressing on schedule, including feasibility level design and studies in support of permitting a filtered (dry stack) tailings storage facility. This conversion from a slurry tailings impoundment aligns with industry leading socio-environmental best practice for tailings management.
- A pre-feasibility study (“PFS”) for an underground paste backfill system was completed in December 2020. The study indicates a paste backfill system will allow ore extraction containing over 100 million pounds of copper and 3.1 million ounces of silver between 2023 and 2031, that would have otherwise been left as unmined pillars. The PFS design has a capital cost estimate ranging from $41 million to $45 million and an increase in operating costs of approximately $7.50 per tonne of ore mined. Capstone management has approved the paste backfill project and work has commenced on procurement of long lead items.
- Initiating “Impact23” Growth Project: exploration excellence, innovative mining techniques and enhanced pillar recovery are areas identified to have growth potential for Cozamin. By 2023, the goal is to further extend mine life, increase environmental and safety standards, and improve operational efficiencies at Cozamin, utilizing mineral resources already discovered in addition to testing new targets.
Brad Mercer, Capstone’s SVP and Chief Operating Officer said, “The LOMP announced today maximizes extraction of the orebody’s high grade core by deferring stoping in this area until the paste backfill plant is in operation in 2023. Projected production averages nearly 60 million pounds of copper per year for seven years at first quartile costs. The Impact23 Growth Project that we are kickstarting today is aiming to demonstrate in a 2023 technical report how Cozamin can sustain these levels of performance well into the 2030s.”
Darren Pylot, Capstone’s President and CEO said, “After 14 years in operation, the best years of Cozamin are ahead. The mine is world-class with sustainable low costs and leading safety and environmental performance entrenched throughout the organization. The growth initiatives are supported by an entrepreneurial fabric at Capstone, as we embrace innovation and technology to create high impact value for our shareholders.”
MINERAL RESERVE ESTIMATE
Table 1 presents Cozamin’s Mineral Reserve estimate for all zones as of October 31, 2020, including the Mala Noche Footwall Zone (“MNFWZ”) and the Mala Noche Vein (“MNV”).
|
Table 1 – Mineral Reserve Estimate as of October 31, 2020 |
|||||||||
|
Category |
Tonnes (kt) |
Copper (%) |
Silver (g/t) |
Zinc (%) |
Lead (%) |
Copper Metal (kt) |
Silver Metal (koz) |
Zinc Metal (kt) |
Lead Metal (kt) |
|
Proven |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Probable |
14,127 |
1.77 |
44.4 |
0.54 |
0.21 |
250 |
20,179 |
77 |
29 |
|
Proven + Probable |
14,127 |
1.77 |
44.4 |
0.54 |
0.21 |
250 |
20,179 |
77 |
29 |
|
Compared to |
+39% |
-1% |
+7% |
+53% |
+314% |
+37% |
+49% |
+112% |
+474% |
|
NOTES: Tucker Jensen, P.Eng., Superintendent Mine Operations at Capstone Mining Corp., is the Qualified Person for this Cozamin Mineral Reserve update. Disclosure of the Cozamin Mineral Reserves as of October 31, 2020 was completed using fully diluted mineable stope shapes generated by the Maptek Vulcan Mine Stope Optimizer software and estimated using the 2020 MNFWZ resource block model created by Garth Kirkham, P.Geo., FGC and the 2017 MNV resource block model created by J. Vincent, P.Geo., formerly of Capstone Mining Corp. Mineral Reserves are reported at or above a US$48.04/t net smelter return (“NSR”) cut-off in conventionally backfilled zones for 2020-2022, a US$51.12/t NSR cut-off in conventionally backfilled zones for 2023+, a US$56.51/t NSR cut-off in paste backfilled zones of Vein 10, and a US$56.12/t NSR cut-off in paste backfilled zones of Vein 20 using three formulae based on zone mineralization. Copper-silver dominant zones use the NSR formula: (Cu*50.476 + Ag*0.406)*(1-NSRRoyalty%). MNFWZ zinc-silver zones use the NSR formula: (Ag*0.259 + Zn*15.081 + Pb*15.418)*(1-NSRRoyalty%). MNV zinc-silver dominant zones use the NSR formula: (Ag*0.203 + Zn*13.163 + Pb*13.233)*(1-NSRRoyalty%). Metal price assumptions (in US$) of Cu = $2.75/lb, Ag = $17.00/oz, Pb = $0.90/lb, Zn = $1.00/lb and metal recoveries of 96% Cu, 84% Ag, 0% Pb and 0% Zn in copper-silver dominant zones, 0% Cu, 60% Ag, 92% Pb and 86% Zn in MNFWZ zinc-silver dominant zones, and 0% Cu, 53% Ag, 79% Pb and 75% Zn in MNV zinc-silver dominant zones. Mineral reserve calculations consider mining by long-hole stoping and mineral processing by flotation. Tonnage and grade estimates include dilution and mining losses. The NSR royalty rate applied varies between 1% and 3% depending on the mining concession, and royalties are treated as costs in mineral reserve estimation. An exchange rate of MX$20 per US$1 is assumed. All metals are reported as contained. Figures may not sum exactly due to rounding. |
LIFE OF MINE PLAN AS OF OCTOBER 31, 2020
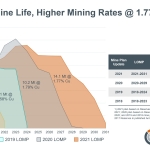
Cozamin’s LOMP has been updated based on the Mineral Reserves presented in Table 1. Compared to previous mine plans since 2018, the 2021 LOMP as shown in Figure 1 shows a longer mine life of 10 years with higher average production and a grade at 1.77%, similar to the 1.79% grade in the 2020 mine plan. This LOMP includes throughput rates of approximately 1.38 million tonnes per annum from 2021 through 2029, followed by declining rates through 2031, before potential additions from Impact23. See Table 2 for a detailed year-by-year mine plan. In its highest grade years, projected copper and silver production from 2021 through 2027 average 58.8 million pounds and 1.70 million ounces, respectively, representing increases of 61% and 53%, respectively, relative to estimated 2020 production as presented in the Cozamin Technical Report dated October 23, 2020.
Figure 1 – 10+ Year Mine Life, Higher Mining Rates at 1.77% Copper
|
Table 2 – Updated Life of Mine Plan 2021 to 2031 |
||||||||||||
|
LOMP – 2021 to 20311 |
2020E2 |
2021E |
2022E |
2023E |
2024E |
2025E |
2026E |
2027E |
2028E |
2029E |
2030E |
2031E |
|
Cu Production (M lbs) |
36.5 |
51.2 |
56.5 |
65.2 |
65.9 |
57.8 |
57.4 |
57.3 |
42.2 |
35.2 |
23.3 |
4.1 |
|
Ag Production |
1.125 |
1.52 |
1.65 |
1.76 |
1.84 |
1.72 |
1.75 |
1.67 |
1.48 |
1.38 |
1.20 |
0.34 |
|
Pb Production (M lbs) |
0.9 |
0.1 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.6 |
6.1 |
5.6 |
4.2 |
6.7 |
10.9 |
9.8 |
5.9 |
|
Zn Production (M lbs) |
11.8 |
0.71 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
1.1 |
9.8 |
7.7 |
6.6 |
12.0 |
16.7 |
20.1 |
8.4 |
|
Tonnes milled |
1.07 |
1.36 |
1.38 |
1.38 |
1.38 |
1.38 |
1.38 |
1.38 |
1.38 |
1.38 |
1.23 |
0.31 |
|
Cu Grade (%) |
1.62 |
1.79 |
1.94 |
2.22 |
2.25 |
1.99 |
1.97 |
1.97 |
1.46 |
1.26 |
0.97 |
0.68 |
|
Cu Recovery (%) |
95.6 |
95.6 |
96.0 |
96.2 |
96.2 |
95.5 |
95.7 |
95.7 |
94.6 |
91.5 |
88.9 |
87.3 |
|
Ag Grade (g/t) |
41.4 |
41.8 |
43.8 |
45.8 |
48.1 |
46.2 |
46.8 |
44.6 |
41.3 |
40.7 |
43.5 |
51.6 |
|
Ag Recovery (%) |
79.1 |
83.8 |
85.0 |
86.3 |
86.3 |
83.8 |
84.4 |
84.6 |
80.4 |
76.5 |
69.9 |
67.0 |
|
Mining Cost ($/t milled) |
26.40 |
22.90 |
24.70 |
29.01 |
28.25 |
28.42 |
28.11 |
27.26 |
28.15 |
27.23 |
26.30 |
22.90 |
|
Milling Cost ($/t milled) |
9.82 |
10.14 |
9.24 |
11.73 |
11.73 |
11.73 |
11.73 |
11.73 |
11.73 |
12.66 |
12.64 |
12.64 |
|
G&A Cost ($/t milled) |
7.10 |
6.54 |
6.84 |
6.86 |
6.86 |
6.88 |
6.88 |
6.88 |
6.86 |
6.87 |
7.63 |
6.54 |
|
C1 Cost3 |
0.96 |
0.96 |
0.95 |
1.03 |
0.96 |
0.88 |
0.95 |
0.98 |
1.20 |
1.27 |
1.50 |
0.57 |
|
Sustaining CAPEX (M$) |
21.9 |
24.5 |
22.3 |
17.1 |
15.9 |
18.2 |
9.9 |
9.3 |
9.5 |
1.7 |
1.4 |
0.3 |
|
Expansion CAPEX (M$) |
– |
13.0 |
32.1 |
1.0 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| NOTES: | ||||||||||||||
|
1. |
Cozamin’s LOMP has been updated based on the Mineral Reserves as of October 31, 2020. Operating and capital costs assume an exchange rate of MXN$20 per USD$1. | |||||||||||||
|
2. |
2020E figures are for 12 months and are a combination of actual results and estimates, as reported in the October 23, 2020 Technical Report, and may not accurately represent actual 2020 figures. | |||||||||||||
|
3. |
C1 Costs assume by-product pricing of Ag = $25.00/oz from 2021 to 2025 and $22.00/oz thereafter, Pb = $0.90/lb and Zn = $1.10/lb from 2021 to 2025 and $1.00/lb thereafter. C1 Costs are net of by-products and includes the 50% silver stream, which provides 10% of silver price to Capstone for 50% of silver produced, and is an alternative performance measure. Please see “Alternative Performance Measures” at the end of this release. |
|||||||||||||
UNDERGROUND PASTE BACKFILL
As part of the technical study described in the Technical Report, Cozamin recently completed a PFS to assess the use of underground paste backfill to decrease the number of pillars needed for geotechnical stability, thereby increasing the mineral extraction ratio. The Mineral Reserve estimate presented in Table 1 includes recovery of approximately 2.2 million tonnes grading 2.09% copper and 44.3 g/t silver that would have been left as unmined pillars without the use of paste backfill.
The proposed paste backfill system includes a tailings filter plant, a paste mixing plant, twin boreholes to deliver paste underground and an underground distribution system (“UDS”). The filter plant, paste plant and conveyor to transport filtered tailings to the tailings storage facility (“TSF”), in relation to the mill and other nearby surface infrastructure, are shown in Figure 2. The system is expected to be commissioned starting in Q4 2022, with ramp-up completed in Q1 2023. PFS design of these facilities was completed by Paterson & Cooke in December 2020, and a Feasibility Study (“FS”) is underway with completion expected in April 2021. Mine planning was completed by Cozamin, with design support provided by a geotechnical consultant, and paste backfill operational guidance provided by AMC Consultants. Preparation of documents to support permit applications for the paste backfill system is underway.
Based on the PFS, capital cost for the tailings filtration and paste backfill system is estimated to range from $40.8 million to $45.0 million, depending on the filtration technology selected, including 25% contingency. The tailings filter plant is required for the conversion to filtered tailings storage, but a portion of the combined capital cost estimate, approximately $17 million, is required for paste production, transport and deposition underground. Average operating costs for tailings filtration and the production, transport and deposition of paste are estimated at approximately $7.50 per tonne of ore mined, partially offset by lower mine development costs.
Figure 2 – Future Location of Tailings Filtration and Paste Plant
TAILINGS MANAGEMENT
Cozamin intends to convert from the current slurry tailings facility that has been safely operated for over 15 years to a filtered (dry stack) tailings facility. Feasibility-level design of the filtered tailings facility is expected to be completed in Q1 2021, and preparations are being made to submit the required permit applications. It is expected that this conversion to filtered tailings will significantly decrease the mine’s socio-environmental, geotechnical and water supply risks, while decreasing water consumption and make-up water costs. The planned paste backfill system will use tailings for paste production, greatly decreasing the volume of tailings requiring an above ground storage impoundment.
OPPORTUNITIES – IMPACT23 GROWTH PROJECT
Capstone is advancing several initiatives with potential to further extend mine life, increase environmental and safety standards, and improve operational efficiencies at Cozamin. The following opportunities are not included in this updated LOMP and do not impact the Mineral Reserve estimate as of October 31, 2020. Capstone’s goal with this project is to target a positive NAV impact, to be underpinned by an updated technical report in 2023, through exploration on drill targets open on each end of the deposit, selective mining techniques to decrease dilution and lower mining costs, and enhanced pillar recovery to leverage the benefits of the planned paste backfill plant.
Exploration Excellence Remains Top Priority
Exploration expansion potential at the MNFWZ remains open in both the West and the East. The 2021 exploration budget of $5 million for 40,000 meters of surface drilling will primarily target expansion drilling in the newly recognized West target area, see Figures 3 and 4. Additional infill drilling to upgrade resources in the down-dip southeast area of Vein 20, and initial testing of new brownfield targets on adjacent vein systems, many with historical production, all within the Cozamin claim block will also be completed.
The MNFWZ West target is an extension of Vein 20 recently identified by an extensive review of historical drilling data and confirmed by initial drill testing of the concept in 2020. The West target is supported by a reinterpretation of the geology in this area and has easy access from both the MNV and MNFWZ infrastructure. Development capacity in 2021 is limited to driving one non-production drift and therefore the East exploration drift has been delayed to 2022. Development of the new West exploration crosscuts will commence in Q1 2021, in tandem with the surface drilling program, with an estimated cost of $1.8 million additional to the drilling program. Once completed, future drilling will shift to underground starting in 2022.
Figure 3 – MNFWZ 2021 Drilling Program
Figure 4 – MNFWZ West Drilling Targets
A detailed Company exploration update including Cozamin and other greenfield targets is scheduled for release in March 2021.
Innovative Mining Techniques for Resource to Reserve Conversion
A study will be initiated in 2021 to assess alternative mining techniques with the objective of lowering costs and dilution to convert resources to reserves from the Indicated Resource shown in Table 3. The current mining methods are Longitudinal Longhole Open Stoping and AVOCA and possible alternatives that will be studied include Cut-and-Fill, Drift-and-Fill and Longhole Open Stoping with ore sorting technology.
Table 3 – Mineral Resources Exclusive of Mineral Reserves and Pillars as of October 31, 2020, Potential Resource to Reserve Conversion Targeted
|
MNFWZ Indicated (I) |
Tonnes (kt) |
Copper (%) |
Silver (g/t) |
Zinc (%) |
Lead (%) |
Copper Metal (kt) |
Silver Metal (koz) |
Zinc Metal (kt) |
Lead Metal (kt) |
|
Copper-Silver Zones |
9,472 |
1.56 |
35 |
0.51 |
0.05 |
148 |
10,796 |
48 |
4 |
|
Zinc-Lead-Silver Zones |
4,138 |
0.38 |
28 |
2.22 |
0.98 |
16 |
3,786 |
92 |
41 |
|
NOTES: Please refer to Table 4 for full details of the Mineral Resource estimate. |
|||||||||
Enhanced Pillar Recovery
A study aimed at enhancing pillar recoveries will commence shortly with short-term and long-term opportunities identified. With the paste backfill plant expected in operation by 2023, pillars in the MNFWZ and throughout historic mining areas at Cozamin are an opportunity for recovery. The following are the main studies within the Enhanced Pillar Recovery Project:
- Cemented Rockfill (CRF). Cozamin is assessing the opportunity to rapidly implement a CRF system to allow the safe and economic recovery of additional pillars. This includes areas mined prior to the planned start of paste backfilling in Q1 2023, and/or where it is not economic to deliver paste. Preliminary results indicate that CRF could be implemented with low capital cost well in advance of Q1 2023, and additional study is underway.
- Used Filtration Equipment. The updated LOMP assumes the start of paste backfilling in Q1 2023 in part because of long lead times for the procurement of tailings filters. Cozamin is assessing a package of used tailings filters that could potentially allow more rapid filter plant construction and paste backfilling starting significantly earlier than Q1 2023.
- Paste Backfill System Optimization. The paste backfill PFS makes a number of conservative estimates for equipment and materials costs, geotechnical stability and other factors. The FS currently underway includes additional laboratory testing and more detailed system design. It is expected that this FS may identify opportunities for capital and operating cost savings, and for increased pillar recovery through optimization of the mine plan.
- Historic Pillar Recovery. Cozamin has left unmined pillars needed for geotechnical stability throughout its mine life, and will continue to do so until paste backfill is available. Typically, conventional backfilled areas have been designed to leave approximately 26% of the total mineralization behind in pillars. Cozamin intends to assess the potential to return to previously mined areas to safely use paste backfill to economically recover pillars left prior to the start of paste backfilling.
Stope Dilution
Stope dilution in the deeper areas of the northwest end of the MNFWZ have been high compared to other longhole open stope mines, driven by narrow veins and local geotechnical conditions. As mining progresses away from this area, an initiative is underway to reduce dilution site-wide through improved engineering, planning, long-hole drill control and optimized explosives design guided by a team of consultants and site experts.
Truckless Headings
An initiative is underway to redesign the upper areas of Cozamin Reserves to ore pass use, increasing safety and efficiency, while increasing air quality, thereby decreasing ventilation requirements in these areas.
MINERAL RESOURCE ESTIMATE
Table 4 presents the Mineral Resource estimate for all zones as of October 31, 2020. Mineral Resource estimates do not account for mining loss and dilution.
Estimated Measured and Indicated Resources have increased by 10% relative to April 30, 2020, with 29.7 million tonnes grading 1.52% copper, 44 g/t silver, 1.10% zinc and 0.32% lead. This change is the result of step-out drilling and infill drilling at MNFWZ that upgraded 1.5 million tonnes of Inferred Resource to Indicated classification, and updated net smelter return (“NSR”) formulae adopted for the cut-off applied, that includes predicted long-term metals prices in line with current industry norms, updated recovery curves, royalties and other operational considerations for MNFWZ and MNV.
|
Table 4 – Mineral Resource Estimate as of October 31, 2020 at a US$50/t NSR Cut-Off |
|||||||||
|
Classification |
Tonnes (kt) |
Copper (%) |
Silver (g/t) |
Zinc (%) |
Lead (%) |
Copper Metal (kt) |
Silver Metal (koz) |
Zinc Metal (kt) |
Lead Metal (kt) |
|
Measured (M) |
407 |
1.24 |
53 |
1.23 |
0.40 |
5 |
698 |
5 |
2 |
|
Indicated (I) |
29,265 |
1.53 |
43 |
1.10 |
0.32 |
446 |
40,799 |
322 |
94 |
|
Total M + I |
29,672 |
1.52 |
44 |
1.10 |
0.32 |
451 |
41,497 |
327 |
95 |
|
Inferred |
13,869 |
0.54 |
39 |
2.23 |
0.74 |
75 |
17,383 |
309 |
103 |
|
NOTES: Mineral Resources are classified according to CIM (2014) definitions, estimated following CIM (2019) guidelines and have an effective date of October 31, 2020. Mineral Resources are reported inclusive of Mineral Reserves. Mineral Resources that are not Mineral Reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability. The Independent Qualified Person for the estimates is Mr. Garth D. Kirkham, P.Geo., FGC., of Kirkham Geosystems Ltd. Mineral Resources are reported using four formulae for NSR based on mineralization. Copper-silver dominant zones use the NSR formula: (Cu*60.779 + Ag*0.485)*(1-NSRRoyalty%). Copper-zinc zones use the NSR formula: (Cu*58.430 + Ag*0.416 + Zn*15.368 + Pb*7.837)*(1-NSRRoyalty%). MNFWZ zinc-silver dominant zones use the NSR formula: (Ag*0.304 + Zn*18.323 + Pb*17.339)*(1-NSRRoyalty%). MNV zinc-silver dominant zones use the NSR formula: (Ag*0.256 + Zn*16.401 + Pb*14.977)*(1-NSRRoyalty%). Metal price assumptions (in US$) used to calculate the NSR for all deposits are: Cu = $3.25/lb, Ag = $20.00/oz, Zn = $1.20/lb and Pb = $1.00/lb. Recoveries used in the four NSR formulae are based on mineralization. Copper-silver dominant zones use the following recoveries: 96% Cu and 85% Ag. Copper-zinc zones use the following recoveries: 92% Cu, 79% Ag, 72% Zn and 42% Pb. MNFWZ zinc-silver dominant zones use the following recoveries: 60% Ag, 86% Zn and 92% Pb. MNV zinc-silver dominant zones use the following recoveries: 55% Ag, 77% Zn and 80% Pb. The NSR formulae include confidential current smelter contract terms, transportation costs and royalty agreements from 1 to 3%, as applicable. An exchange rate of MX$20 per US$1 is assumed. Totals may not sum exactly due to rounding. The NSR cut-off of US$50/tonne is based on historical mining and milling costs plus general and administrative costs. The Mineral Resource Estimate encompasses both the MNFWZ and the MNV. Drilling campaigns from 2018 have focused on the MNFWZ and no drilling has been performed on the MNV since 2017. The Mineral Resource considers underground mining by longhole stoping and mineral processing by flotation. No dilution is incorporated in the Mineral Resource. All metals are reported as contained. Mineral Resource estimates do not account for mining loss and dilution. These Mineral Resource estimates include Inferred Mineral Resources considered too speculative geologically to apply economic considerations for categorization as Mineral Reserves. However, it is reasonably expected that the majority of Inferred Mineral Resources could be upgraded to Indicated Resources. |
NATIONAL INSTRUMENT 43-101
A National Instrument 43-101 (“NI 43-101”) Technical Report will be prepared to summarize the Mineral Resource and Mineral Reserve estimates by the Qualified Persons and will be filed on SEDAR within 45 days of this news release.
Readers are cautioned that the conclusions, projections and estimates set out in this news release are subject to important qualifications, assumptions and exclusions, all of which will be detailed in the 2021 Technical Report. To fully understand the summary information set out above, the 2021 Technical Report that will be filed on SEDAR at www.sedar.com should be read in its entirety.
QUALIFIED PERSONS
The following Qualified Persons, as defined by NI 43-101, are independent from Capstone (except as noted below) and have reviewed and approved the content of this news release that is based on content from their respective portions of the 2021 Technical Report:
- Gregg Bush, P.Eng. (Non-independent)
- Leslie Correia, Pr.Eng., Paterson & Cooke Canada Inc.
- Jenna Hardy, P.Geo., FGC, Nimbus Management Ltd.
- Tucker Jensen, P.Eng., Capstone Mining Corp. (Non-independent)
- Garth Kirkham, P.Geo., FGC, Kirkham Geosystems Ltd.
- Chris Martin, CEng MIMMM, Blue Coast Metallurgy Ltd.
- Vivienne McLennan, P.Geo., Capstone Mining Corp. (Non-independent)
- Josh Moncrieff, P.Geo., Capstone Mining Corp. (Non-indep
Contacts
Jerrold Annett, VP, Strategy and Capital Markets
647-273-7351
jannett@capstonemining.com
Virginia Morgan, Manager, IR and Communications
604-674-2268
vmorgan@capstonemining.com